Jan's Computer Basics:
Processing: Physical Components
There are several physical components of a computer that are directly involved in processing. The processor chip itself, the memory devices, and the motherboard are the main ones.
| Microprocessor- | a single silicon chip containing CPU, ALU, and some memory. The ROM (Read Only Memory) contains the minimum instructions that the computer needs to get started, called booting. What a user does on the computer cannot change what is stored in ROM. There may also be another chip dedicated to calculations. The microprocessor chip is located on a large circuit board called the main board or motherboard. The physical size of a computer chip is very small, as the ant below illustrates. 
Processor speed is measured in Megahertz (MHz) or Gigahertz (GHz). |
Memory Devices:
| Vacuum tube - |

Copyright (c) 123RF Stock Photos |
| Core - | Small metal rings. Magnets tip a ring to left or right, which represents on and off. Relatively slow even way back when this was used. |
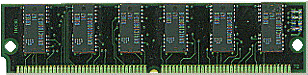
| Semiconductor - | Integrated circuit on a chip. This is what modern computers use for memory. Pictured below is a 72-pin SIMM card.
|
Memory Speed
RAM (Random Access Memory) is what the computer uses as Main Memory. Memory speed measures the time it takes to move data in or out of memory. It is measured differently for different kinds of memory chips:
- in nanoseconds (ns )
(smaller is faster) for EDO and FPM
1 ns = 1 billionth of a second. - in megahertz (MHz) (higher is faster) for SDR SDRAM, DDR, SDRAM, and RDRAM.
The capacity of a memory chip is measured in megabytes or gigabytes. For example, 256 MB of RAM is required to run WindowsXP and 512MB is much better. For Windows 7 the requirements are 1 gigabyte (GB) RAM (32-bit) or 2 GB RAM (64-bit).
Several such memory boards can be installed in the computer to increase the amount of RAM available. Motherboards have only so many slots for memory so there are limits. Some motherboards require that all slots be filled and that all slots contain the same size memory board. It can get frustrating as there are no warning labels about this!