Jan's Working with the Web
Interface
When you open a program, the window that you see on your computer screen has a few features in addition to the standard window parts. What is different with browsers?
Interface:  IE
IE
Internet Explorer is fading from use. Microsoft's newer browser is Edge, which comes with Windows 10.
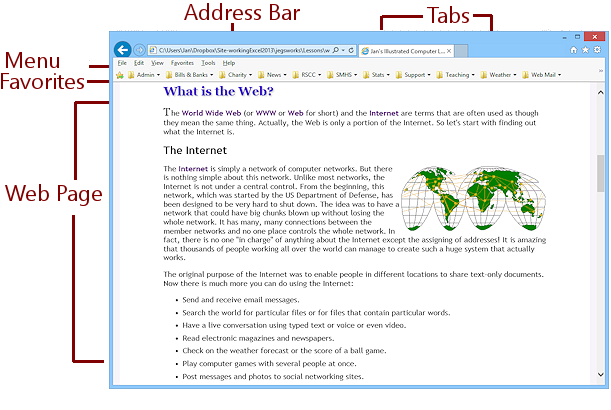
The new default is to hide the bars - Menu, Favorites, and Status. But
you need the menu to find some commands. Most commands are available also from the Tools button ![]() , which has a gear shape.
, which has a gear shape.
When the Status Bar is hidden, a pop-up version shows any messages.
Interface:  Chrome
Chrome
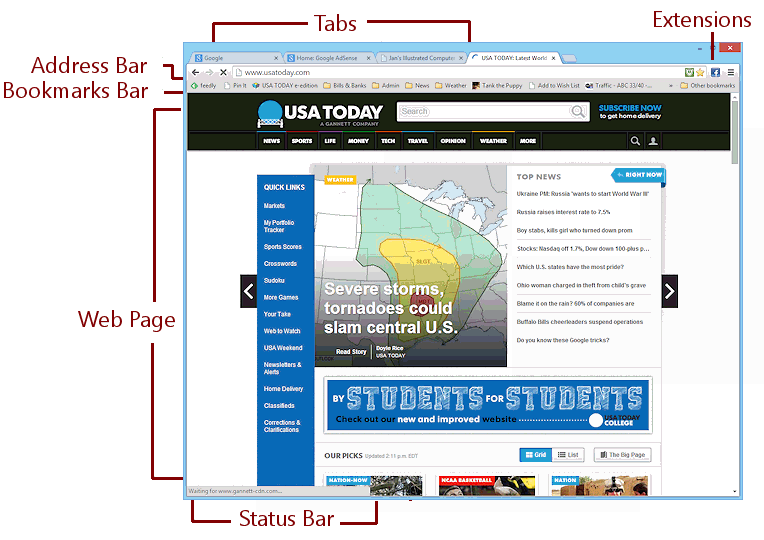
Chrome does not have a Menu Bar at all. There is a Customize and control button ![]() that opens a menu of commands. This button is sometimes called the 'hamburger' button for its three lines, like a hamburger patty inside the bun.
that opens a menu of commands. This button is sometimes called the 'hamburger' button for its three lines, like a hamburger patty inside the bun.
Its Status Bar pops into view when it has something to say.
Interface:  Firefox
Firefox
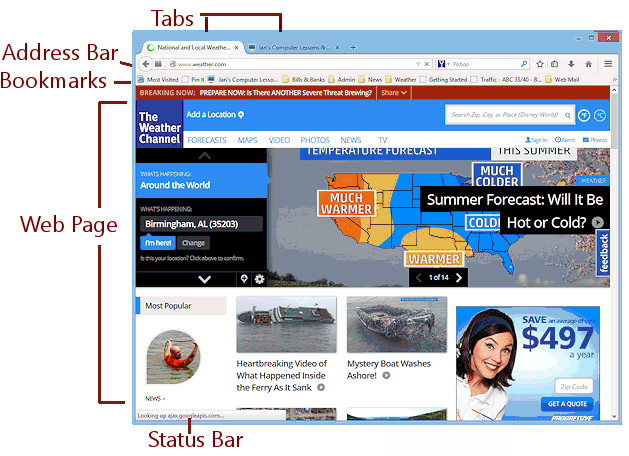
Firefox tucks the commands into a menu button ![]() that opens a palette of icons. This button is sometimes referred to as the 'hamburger' button because its three lines are like a hamburger patty in a bun.
that opens a palette of icons. This button is sometimes referred to as the 'hamburger' button because its three lines are like a hamburger patty in a bun.
It's Status Bar shows only when there is something to report. The tabs can be above or below the Address Bar and Bookmarks Bar.
Parts Special to Browsers
What features are special to browsers?
-
Address Bar:
 IE:
IE: 
 Chrome:
Chrome:
 Firefox:
Firefox: 
This text box shows the address of the page currently displayed in the browser. You can type an address in the box to go to a different web page, if you know its URL. AutoComplete may offer choices as you type.
All of our example browsers now let you type search words in the Address Bar and press ENTER to do a search using the default search service. This way you do not have to have a special Search text box.
Address bar also found in: File management windows, but usually the address is to a document on the computer or on a removable drive instead of out on the Internet.
-
Tabs:
 IE:
IE: 
 Chrome:
Chrome:
 Firefox:
Firefox: 
There is a tab for each open web page instead of using a separate window for each page. The page's Title shows on the tab, at least as much as will fit. Hover over the tab and a ScreenTip shows the full page title. Browsers were the first programs to offer this style of interface.
Tabs also found in: Newer versions of other programs show a tab for each open document.
-
Home button:



Returns to the Home page you set in the Options for the browser. Different browsers place this button in different spots.
Home button also found in: Help windows to return you to the table of contents.
-
Back and Forward buttons:



Take you through the list of pages you have recently viewed.
Back and Forward buttons also found in: File management and Help windows to help you get to places you have been before.
-
Refresh/Reload button:



Reloads the web page with up-to-date content. This is especially helpful on pages that change frequently, like news or stock prices or sports scores. Such pages may automatically refresh on a timer.
This button is found at the right end of the Address box or beside the Back and Forward arrows.
The F5 key on the keyboard also refreshes the window.
-
Stop button:



Instead of having a separate button, while a page is loading, the Refresh button changes to the Stop button. While it is in the X shape, clicking the button stops loading the current page. Restart a slow loading page: When the page fails to load correctly, or at all, click the
Stop button and then Refresh. The
page often loads quickly. This method often works better than a simple Refresh.
Restart a slow loading page: When the page fails to load correctly, or at all, click the
Stop button and then Refresh. The
page often loads quickly. This method often works better than a simple Refresh.
The current fashion is for browsers to maximize the space for the actual web page by tucking away a lot of features that used to be out in plain view, like the Menu Bar, Status Bar, and Title Bar. You may be able to choose whether or not to show these features.
Plug-Ins, Add-Ons, and Extensions:
You may see extra toolbars or buttons in your browser's interface. Depending on the browser and on what the extras do, these may be called plug-ins, add-ons, or extensions. Each of these adds a function of some sort to your browser. Some add a new part to the interface, like a toolbar or a button.
For example, sites for searching, shopping, games, social networking, and news may offer a toolbar that makes it easy for you to use their services. A program on your computer may put a button on your browser to connect to its own web site for services, like social networking sites, web-based printing, uploading photos, downloading files, or finding updates for the program.
Examples:
Add-on toolbars: 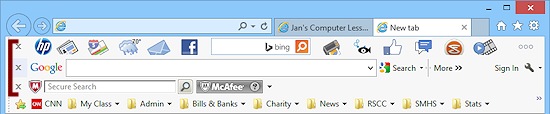 |
Bing - comes with a large
selection of buttons to various services and sites |
Add-on buttons for programs:   |
| Facebook - Social
networking site |
In the next lesson we will look at some settings and see how to manage these plug-ins/add-ons/add-ons/extensions.

How to: Show/Hide Bars in IE
How to: Show separate rows for Address Bar and Tabs in IE
The same right click menu has a command to Show tabs on a separate row.
Having the tabs on the same level as the Address Bar limits the space for both of them. Separate rows gives lots of room for addresses but does not increase the size of a tab.
Address Bar and Tabs on separate rows