Jan's Computer Basics:
Applications: Word Processing
There are many different kinds of applications, all with lots of spiffy features.
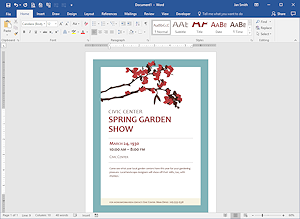 Word processing is the application that is used most often and most widely. We will start with it to learn about the terms and features that are common to most applications, as well as some that are specific to word processing. Then we will look at other major applications and what they do.
Word processing is the application that is used most often and most widely. We will start with it to learn about the terms and features that are common to most applications, as well as some that are specific to word processing. Then we will look at other major applications and what they do.
Examples of word processing programs: Microsoft Word, WordPerfect, Lotus WordPro, and Open Office Writer.
Word Processing
Word processing is the most used computer application!
 It has replaced the typewriter as the main way words are put on paper. Documents can be revised and corrected before they are ever printed. An existing document can be used as a template, or pattern, for a new one. So the user doesn't have to recreate standard documents from scratch each time. This is a major time-saver and helps keep things consistent.
It has replaced the typewriter as the main way words are put on paper. Documents can be revised and corrected before they are ever printed. An existing document can be used as a template, or pattern, for a new one. So the user doesn't have to recreate standard documents from scratch each time. This is a major time-saver and helps keep things consistent.
| Purpose: |
|
| Main advantage: |
|
Steps to produce a document
- Create
- Edit
- Format
- Save (often!!)
Let's look at the terms involved in these steps more closely.
Most of these terms also apply to the other standard applications, so we will not redefine them for all.
Create
You create a document when you open a blank document and enter text.
Features/Terms:
| Word wrap - | Automatically wrapping the text to the next line so it all fits within the screen's width. Change the size of the screen and the text moves to fit in the space. |
| Cursor - | Symbol for where text will appear like: |
| Enter text- | Type new text |
| Scrolling - | Moving document around within window |
| Select - | Highlight text, usually by dragging. Commands and keystroke combinations will apply to the selected material. |
| Edit - | Make changes |
| Cut - | Remove selection from document and store temporarily on the Clipboard, which is a section of computer memory. The Windows Clipboard can hold only one thing at a time. The Office Clipboard from Office XP and later versions can hold many items. |
| Copy - | Duplicate selection onto Clipboard |
| Paste - | Place contents of the Clipboard at cursor location |
| Undo - | Reverses whatever change you just made Some programs will only "undo" the last change. Others keep a list and can undo more, depending on how many changes the program tracks. |
| Insert - | Add text at location without overwriting existing text |
| Overwrite - | Typing overwrites existing text, replacing whatever characters were there already |
| Delete - | Remove text (not saved anywhere) |
| Search - | Look for specific word(s) or character(s) in the document |
| Replace - | Can replace specific word(s) or character(s) with stated text |
| Template - | Document that serves as a pattern for a new document |
| Thesaurus - | Looks for synonyms for selected word |
| Spelling check - | Looks for spelling errors |
| Grammar check - | Looks for grammar/style errors (of limited help) |
Do it! Simple Text
It's time to play! You can use the text box below to play with basic word processing skills. There are no buttons to use so I have written directions on the left using some standard key combinations. Of course, some programs may use different ones.
You will have to scroll the Directions area to see all of the steps.
Directions:
- Cursor: Click in the text box at the right. Do you see the cursor shape
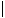 ? This is where your typing will appear. Notice that your mouse pointer
has a different cursor shape
? This is where your typing will appear. Notice that your mouse pointer
has a different cursor shape 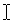 when it is over the web page text.
when it is over the web page text.
 Move the cursor:
Move the cursor:
Use the arrow keys on the keyboard to move the cursor to different locations.
-
 Enter text: Type some text of your
own to add text the text box until the text starts to scroll up. Use the ENTER
key to start a new paragraph and type some more. Create enough text and
paragraphs that a scroll bar appears at the right of your text.
Enter text: Type some text of your
own to add text the text box until the text starts to scroll up. Use the ENTER
key to start a new paragraph and type some more. Create enough text and
paragraphs that a scroll bar appears at the right of your text.
- Scroll: Use
the scrollbar to shift which lines are showing in the text box
-
 Edit: Select some text by dragging the mouse across it.
Delete the text by pressing the DELETE key.
Edit: Select some text by dragging the mouse across it.
Delete the text by pressing the DELETE key.
-
 Undo: Before clicking out of the text area, restore the deleted text by holding down the CTRL key while you press the Z key once. Then release the CTRL key. (Key combo CTRL + Z)
Undo: Before clicking out of the text area, restore the deleted text by holding down the CTRL key while you press the Z key once. Then release the CTRL key. (Key combo CTRL + Z)
In a regular program you can choose Edit > Undo from the menu.
- Cut: Select
some text. Cut the text with the key combo CTRL + X. Move the cursor to a new
location.
- Paste: Use
the key combo CTRL + V to paste what you cut into a new location.
- Copy: Select
some text. Copy the text with the key combo CTRL + C. Move the cursor to a new
location and paste it there.
- Undo: Reverse
what you just did with the key combo CTRL + Z.
-
 Insert: Move your cursor to the middle of some existing
text. Start typing. Press the INSERT key, type, press the INSERT key, and
type some more. What happens depends on whether INSERT is on or off. When
INSERT is on, your new typing appears between the existing characters. If
INSERT is off, the new characters replace the old ones (overtyping).
Insert: Move your cursor to the middle of some existing
text. Start typing. Press the INSERT key, type, press the INSERT key, and
type some more. What happens depends on whether INSERT is on or off. When
INSERT is on, your new typing appears between the existing characters. If
INSERT is off, the new characters replace the old ones (overtyping).
For a full set of lessons on word processing, go to the section: Working with Words![]()
Format
Once a document has been created, or during the process, you arrange how it will look by selecting the kind of letters and their sizes and colors, how much space is left and where, how things line up. All of this makes up the formatting of the document.
Features/Terms:
| Typeface - | Set of characters of similar design like: |
||||||||
| Point size - | One point = 1/72 of an inch like: 12 pt 18 pt 24 pt 36 pt |
||||||||
| Font - | Combo of typeface and point size, includes styles such as bold, italics, underline | ||||||||
| Margins - | |||||||||
| Justification - |
|
||||||||
| Spacing - | |||||||||
| Borders/shading - | |||||||||
| Headers/footers - |  Info to repeat on each page Info to repeat on each page |
||||||||
| Style set - | 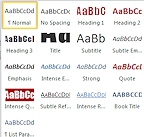 Saved sets of formats to reuse in different places in the document and with different documents. Possible confusion with 'style' used for bold, italics, and underline! Saved sets of formats to reuse in different places in the document and with different documents. Possible confusion with 'style' used for bold, italics, and underline! |
||||||||
| Columns - | |||||||||
| Tables - | |||||||||
| Graphics - |  Pictures and charts Pictures and charts |
When a document is finished, you can print it onto paper, if you have a printer connected to the computer. You will have several choices to make as part of the printing process:
Features/Terms:
|
Number of copies/pages to print |
||
|
Orientation: |
|
|
| Portrait | Landscape | |
| Quality: | Most printers can print with a low quality (Draft) as well as with better quality levels. |
|
|
Print Preview: |
Shows you how it will look in print |
|
For a full set of lessons on word processing, go to: Working with Words![]()
