Jan's Working with Databases
Basics: Interface
The user interface for Microsoft Access looks much the same as in other programs, with the usual bars: Title bar, ribbon, Status bar, task panes. There is one obvious difference from other Office programs. In the work area, the Navigation Pane is at the left edge of the window as long as the database is open. The Navigation pane shows the objects that are in this database, like tables, queries, forms, and reports.
The work area to the right of the Navigation pane holds windows for all of the open objects, like tables or forms.
Context ribbon tabs appear only when they can be used by the active window. For example, the Form Design Tools tabs appear only when a form is showing in Design view.
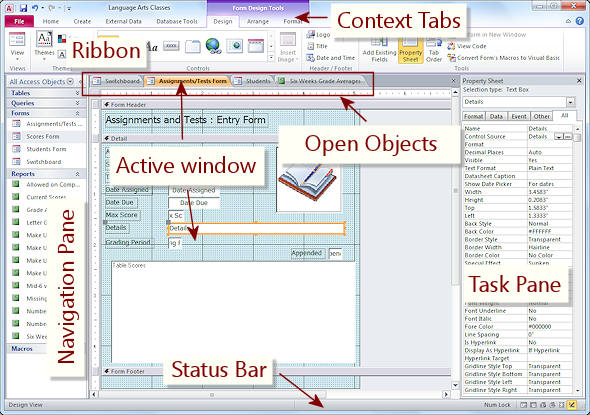
Microsoft Access 2010: Active window shows a form in Design view
and a Task Pane is showing
Database Terms
| Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
| object |
Something used to store or refer to data - table, query, form, report, macro, and module. |
| field | Holds a single item of data, like a last name or a price. Would appear in a column in a table or in a control on a form or report. |
| record | A set of fields that are about the same 'thing', like product or employee information. Shows as a single row in a table. |
| table | Records listed in rows and columns. |
| query | Pulls together fields from one or more tables or queries to sort, filter, or calculate with them. |
| form | Displays the fields from a single record to make them easier to read and edit. |
| report | Formats data for creating totals or for printing. |
| macro | A memorized set of database actions that can be reused, like opening a particular form when a button control is clicked. |
| module | A collection of related functions defined by the user and subroutines, all written in Visual Basic. |
| datasheet | Display of table or query results in row/column layout. |
| sort | Arrange records in a different order. |
| filter | Show only the records that match the certain criteria. |
| control | An item that is part of the design of a form or report, like a text box, a label, a subform, or a dividing line. |
