Jan's Working with Windows 10:
Files: Backup Data
Now that you have created some documents, you need to consider how to safeguard your files. Nothing is like that horrible sinking, sick feeling that you get when you realize that you've destroyed/damaged/lost the one and only copy of something that took days to create. You need to do some basics on your own to avoid a lost-file disaster.
Since removable disks are easy to lose or damage, you should have at least one copy of your work besides the working copy on your Class disk. Such a copy is called your backup, so we will call this disk the Backup disk.
When working with your own computer at work or home, your files will normally be stored on that computer's hard disk or SSD disk. To back up those files, you have several choices. Each is useful in certain circumstances. The more copies you have, the more protected you are from lost or damaged files.
General Backup Choices
These could be done manually or automatically.
- Same computer: Copy files to a separate folder on the same computer.
- Different local device: Copy files to an external hard drive, a removable USB disk, or a rewritable CD or DVD.
- Disc: Burn a set of finished files to a CD or DVD.
(No longer can be edited) - Network: Upload the files to network storage space, to another computer on the network where you have logon privileges, or to storage at a course management site.
- Online: Upload the files to online storage, like Dropbox, OneDrive, or Google Drive.
Recommended for this class: Have three copies that you keep synchronized
- Working copy on a USB flash drive
- Backup copy on a different USB flash drive
- Online copy on a service like Dropbox, OneDrive, or Google Drive
Think about how important the files are and hard it would be to do the work over again. The more difficult it will be to recreate the file, the more copies you need in more locations.
The hardest part of any backup plan is remembering to do it! That's why apps that do this automatically are so popular.
File History: Windows 10 comes with the File History feature, which can automatically make copies of changed files in your Libraries folders. You must turn this feature on. By default Libraries includes the current user's Documents, Pictures, Music, and Videos folders. You can make Libraries show in File Explorer and then add other folders to the Libraries to make File History keep track of them. But...the copies are saved to an external hard disk, which you will have to purchase. Get as big a drive as you can! File History can fill up a drive fast.
Online storage: Many free online storage services will automatically synchronize files in a folder that the app puts in your User folders. That keeps your local hard disk copy and your online copy matched up. Very important! Such sites also let you access your files from any computer that has Internet access, including a tablet or smart phone. You need apps on the device that can open and edit those files. Each account will have a user name and password.
Dropbox: 2 GB free with several ways to earn extra free space.
OneDrive: 15 GB free with a free Microsoft account.
Subscribers to Office 365 have 1 TB free.
Google Drive: 15 GB free to share with your Google Drive, GMail, and Google Photos. A Google account through school or work has 30 GB.
Note: GB = gigbyte = about 1000 MB, TB = terabyte = about 1000 GB
Backup software: If you have a lot of files to backup, you will want to think about using some kind of backup software that will do the work automatically in the background. Backup software can do local backups to a separate drive or even online backups. There are free and paid versions. The online features usually require using a paid version. You might get unlimited storage with a paid version of an app like Carbonite.
![]() Warning: Losing access
Warning: Losing access
Do not store the only copy of important files in locations where you might lose access. You might quit your job or get unexpectedly fired. You will eventually finish a class or graduate from school. An online storage company might go out of business or you might forget to pay the bill.
| |
Step-by-Step: Manual Backup Copy |
|
| What you will learn: | to create a backup copy |
Start with:![]()
![]()
![]()
Create the Backup Copy Yourself
 Insert your Class disk into its drive.
Insert your Class disk into its drive.
If necessary, display the contents of the drive in a File Explorer window.
 Refresh the view with the key combo: F5
Refresh the view with the key combo: F5
There are other methods but the key combo is fastest for a PC.Be sure that the disk is your Class disk. This is your source disk for the sequence to follow.
-
 Insert you other USB flash disk (the Backup drive or destination disk) into a different USB port.
Insert you other USB flash disk (the Backup drive or destination disk) into a different USB port.  Problem: Do not have access to two USB ports
Problem: Do not have access to two USB ports
Any reasonably recent PC will have more than one USB port. There are usually two on the front and more on the back. Of course your ports may all be in use! A Windows 10 tablet won't likely have two USB ports and a laptop might not either.
Solution: Copy your files to a temporary location on the hard disk. Safely remove the source disk. Insert the destination disk. Copy and paste from the hard disk to the destination disk.
- If necessary, display the contents of the drive in a File Explorer window.
- In the window for your Class disk, select the files or folders that you wish
to copy to the second disk.
 Use the key combo CTRL + C to copy what
is selected.
Use the key combo CTRL + C to copy what
is selected.
- Switch to the window for your second device.
 Use the key combo CTRL + V to paste
your files to this device.
Use the key combo CTRL + V to paste
your files to this device.
The files are copied. It can take a long time when you are copying a large amount of data. You will see a progress bar in that case.
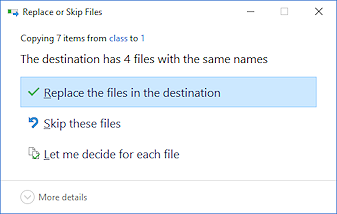
 Problem: Files already exist
Problem: Files already exist
A message box will ask you what to do about duplications. Choose to replace the files to have an exact duplicate. Skip these files to copy only new files. Choose 'Let me decide for each file' when there are not too many files and you need to pick only certain ones. Or you can press the ESC key to cancel the whole operation and do something else. One option is to create a new folder to hold the current copies. Just be careful to name the folders that hold different versions in a way that makes it clear which is which. Including the date is one way to keep things clear.
