Jan's Working with Databases
Glossary
If you don't see the term you are looking for, use your browser's Find command to search for it. Perhaps your term is used in a definition.
Each term is linked back to the appropriate lesson. If you don't see the term on that page, use your browser's Find command to search for it.
# or symbol
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
# or Symbol
- #Deleted
- The record has been deleted.
- #Div/0!
- Calculation is trying to divide by zero. Check your expressions for calculations for the possibility of current AND future records resulting in division by zero.
- #Error
- Access cannot evaluate the expression. There are a number of
reasons possible.
- Circular reference: Using a control's name in an expression that defines values for the same control
- Aggregate functions: Field name misspelled or there are not enough arguments given
- Default value in a table or form: Wrong Data Type or Field Size for the field
- Query: Result of calculation is larger than the Field Size allows
- #Locked
- Access keeps other users from editing records that you are editing. In addition, if you have multiple Access databases open at once on your computer, Access treats each one as a separate user. So you can only edit records from one database at a time. Also, Access locks out groups of records at a time, not just single records. How many at a time depends on the size of the records.
- #Name?
- The name that you typed for a source is not valid.
- Misspelled name of field
- Omitted the equals sign (=) in an expression in a form or report
- Source has been deleted
- #Num!
- The value is too large to be stored in the field due to the Data Type or Field Size
A
- action
- An action is a commands like "Open Form", "Close", "Save", that you want to happen when a macro runs
- active cell
- The active cell in a datasheet or spreadsheet receives the action or keystrokes. In an Excel spreadsheet the active cell has a dark, wider border. In a datasheet the Row Selector will have an arrow in it and the cursor will be blinking in the active cell.
- active tab
- The ribbon tab or window tab that is currently open for use.
- action query
- A query which performs an action with the records/fields selected by the query. Action queries include Make-Table, Append, Delete, and Update queries.
- aggregate function
- A function which groups values together, such as a sum, average, count, maximum, or minimum.
- align
- Controls: To line up controls evenly, either horizontally or vertically.
- Text in a control: To arrange text as centered or aligned to the left or right of a control.
- Allow Zero Length property
- A property of a field that allows a length of zero, like "". This is not the same as a null value, which means the field has not been touched at all.
- Append query
- A query which add records to an existing table.
- Application Part
- A template for an object in Access 2010. Some will create not only a table but also queries, forms, and reports that are based on that table.
- argument
- Function: Choices that must be made for a function to work. For example the IIF function requires 3 arguments: the condition to test for, what to show if the condition is true, and what to show if the condition is false.
- Design dialog: A secondary choice that you must make, such as choosing Currency after choosing Number as the data type. Or in the Macro Builder, once you choose "Open Query" as the action, you must specify which query to open. The name of the query is an argument.
- attached
- A label is attached to its matching control. Some labels stand alone.
- Attachment data type
- Stores one or more images or documents. Some file formats will be compressed for storage.
- Attachment control
- A control for an Attachment data type field, which can hold several files like images or documents.
- Auto Activate
- For an OLE object, the property that determines what program will be used to open the object when it is double-clicked
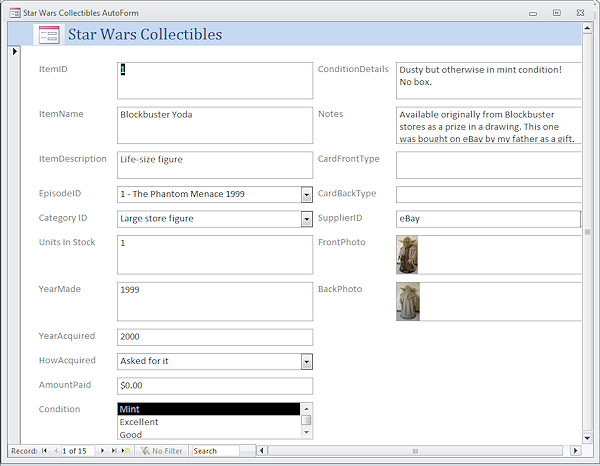 AutoForm
AutoForm- Creates a default form immediately, using all of the fields in the selected table or query.
- AutoFormat
- A combination of formatting choices that is saved as a style and can be applied through the AutoFormat dialog.
- AutoNumber data type
- Automatically numbers a new record
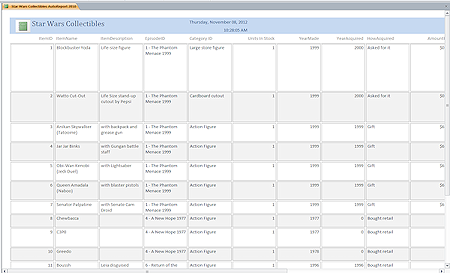 AutoReport
AutoReport- Creates a report immediately showing all of the fields in the selected table or query into a datasheet. (This is different from earlier versions of Access.) The Report Wizard does a better job.
- Avery
- A company which produces a number of commonly available types of labels and other office products.
- Avg
- A function which averages the values.
Syntax: Avg(expr) where expr stands for a string expression that identifies the field whose values you want to average. Avg adds all the values and divides by how many values there were. Avg ignores Null values.
Examples:
Avg([Price])
Avg(([Score]+[Bonus])
B
- background
- What appears behind/underneath the controls or text in a control on a form or report. A background can be a color or an image.
- Backstage View
- A view in Office 2010 and 2013 programs which contains commands that apply to the file as a whole, such as Save, Print, Open. Print Preview is part of Print in other Office programs, but Access uses a window just like for a table, form, or other object.
- backup
- A copy of a file which is made in case damage occurs to the original.
- Best Fit
- A column that is sized automatically to show the widest item in the column.
- blank
- A field which appears to have nothing in it. A blank field may be Null or contain a zero-length string.
- bound column
- The column in a Lookup list that has the value that is actually stored in the field.
- bound control
- A control on a form or report which shows the values from a particular field.
- bound object frame
- An OLE frame which holds an object that is a value for a particular field.
C
- calculated control
- A control that shows a value that is calculated using field values or values from other calculated controls. The values may be text or numbers.
- calculated field
- New with
 Access 2010. New data type, Calculated. You can write an expression that uses other values in the table to calculate a new value. You cannot compare different fields and you cannot use fields from other tables or queries. The calculation can produce text, numbers, or a combination, like a complete name or address.
Access 2010. New data type, Calculated. You can write an expression that uses other values in the table to calculate a new value. You cannot compare different fields and you cannot use fields from other tables or queries. The calculation can produce text, numbers, or a combination, like a complete name or address. - calculated value
- An expression uses values from existing table
or query fields and calculates a new value. The result can be text or numerical. All versions of Access can calculate a new field in a query.
Example with text data:
= [LastName]&", "&[FirstName] produces a combined name like, Hatler, James
Example with number data:
= ([AverageTests]+[AverageHomework])/2 produces a single number like, 93.5
Example including fixed text:
="Your score was "&[Score]&"." produces text like, Your score was 88. - Can Grow Property
- A property of a control or section of a form or report which allows it to enlarge if the value to display does not fit.
- Can Shrink Property
- A property of a control or section of a form or report which allows it to reduce in size if the value to display does not need all of the space allowed in Design View.
- Caption Property
- A property of a field which defines what will show in the table's column heading for this field instead of the field name. The caption value also is used in the label for the field's control on a form or report.
-
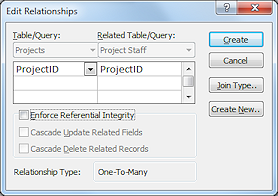 cascade
delete
cascade
delete - Occurs when a record is deleted and all related records in other tables are automatically deleted also. The tables must have a relationship that requires Referential Integrity to be enforced AND that allows cascading deletions. These choices are in the Edit Relationships dialog.
- cascade update
- Occurs when a record's field value is updated and all related records in other tables are automatically updated also. The tables must have a relationship that requires Referential Integrity to be enforced AND that allows cascading updates. These choices are in the Edit Relationships dialog.
- cell
- The intersection of a row and a column
-
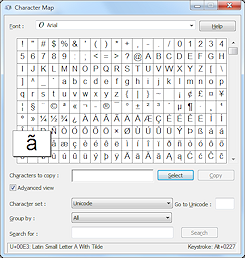 Character
Map
Character
Map - A program that comes with Windows which displays
all of the characters available in the selected
font. The window also shows the keyboard code to use
for the character.
 chart
chart- A visual display of data like a bar chart or pie chart.
- Chart Wizard
- A sequence of dialogs that leads you through the process of creating a chart.
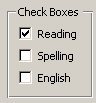 check box
check box- An box shape which is either clear or checked, by clicking on it. Used to offer several choices on a form. Usually you can choose one or many of the choices, unlike a radio button for which you can only choose one in the group.
- Child
- A subform/subreport is the Child in relationship to the main form/report, which is the Parent.
- circular reference
- An expression which refers to the control or query column that the expression itself is in creates a circular reference error.
- clip
- A value for the Size Mode property of an image, which results in showing only the part of the image that fits in the control, starting from the upper left.
- column
- Datasheet: A vertical set of cells, running from the top of the datasheet all the way to the bottom of the datasheet.
- Report: A listing of records in two or more separate sets on one page. Records can run down the column and then across to the top of the next column, or they can go across in a row and then drop down to the next row.
- column heading
- Excel: A button which shows the letter name of the column
- column selector
- A button at the top of a column in a datasheet which shows the field's name or Caption property value. Clicking the button selects the entire column.
- column width
- The horizontal size of a columns of cells.
- combo box
-

 A
control which opens a drop list of choices. It may
show several fields but only stores the value from
one field.
A
control which opens a drop list of choices. It may
show several fields but only stores the value from
one field. - compact
- To remove wasted space from a file, resulting in a smaller file size.
- compiled
- When a program is compiled, it is turned into machine code (1's and 0's). This protects the program from being changed by unauthorized people and keeps secret the methods used by the program .
- concatenation
- Combining text and/or values into one text string. For example, you might combine the separate fields for a name (firstname, middlename, lastname) into a single calculated field called Name, which could produce names that are easier to read in reports, like: Johnson, Ronald Ferguson or Ronald Ferguson Johnson.
- constant
- A value that remains the same. Numeric constants include fixed mathematical values like pi (π). System-defined constants include True, False, Null.
- context tab
- A ribbon tab that appears only when its commands can be used. For example, the Form Design Tools tabs appear only when a form is in Design View.
- continuous forms
- Displaying database forms one after the other instead of as separate pages.
-
 control
control - An object that displays data on a form or report.
- Control Source property
- A property of a control on a form or report that
specifies where the value comes from. It is a value
from one of the fields in the source for the form or
report, or else is calculated using those values.
 Controls palette
Controls palette- The tab group that contains tools for creating controls on a form or report.
- Count function
- An Access function which counts the number of
records that have a value in the selected field.
Syntax: Count(expr)
where expr is a string expression which identifies the field whose values you want to count or does a calculation using data from that field. You can "count" text fields as well as number fields.
Count does not count Null fields unless expr is an asterisk, *. - Count(*)
- An Access function which counts all of the records, including nulls.
- criteria
- The rules for the values that must be matched in
a datasheet filter or query criteria in Query Design View.
For example, Price > $25 or LastName starts with G.
- criterion
- Singular form of criteria. (Just one rule)
- crop
- To cut off part of the value in a control, especially an image. This can happen unintentionally when there was not enough space allowed in the control or enough space on the form or report.
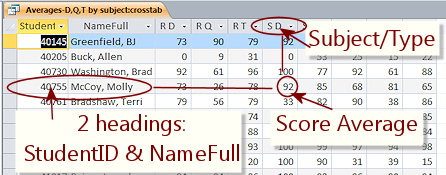 Crosstab query
Crosstab query- A crosstab query calculates one of the aggregate
functions based on several fields. One or more
fields have their values at the left of the
datasheet as row headings. Another field has its values across the top as column headings. The cells
in the middle are the "total", which can be a Sum,
Avg, Count, or one of the other aggregate functions.
The illustration shows Molly McCoy had an average of 92 for the daily Spelling grade. There were also averages for quiz and test grades in all three subjects, Reading, Spelling, and English.
-
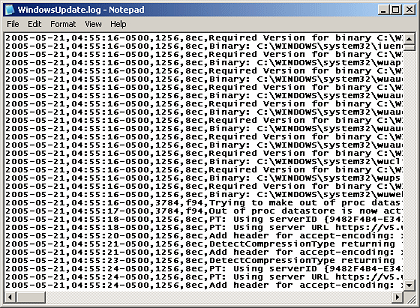 CSV
format (Comma Separated Values).
CSV
format (Comma Separated Values). - This text database format puts a comma between each field, like the example at the right. The file may use csv as the file extension, like mydata.csv
- Currency data type
- Stores a numbers as money.
- custom dialog
- A dialog which receives choices for a parameter query, usually as part of opening a form or report that is based on the query.
- customize ribbon
- Access 2010: Add or remove items from a custom ribbon or custom ribbon tab group.
D
- database
- A method of keeping records which are made up of fields. A database can be written by hand, kept in a ledger or address book, or use software.
- database application
- A database which has as its main purpose the entering and viewing of data. Users do not make changes to the features of such a database.
- database programmer
- A person who designs databases and writes code to create and control them. A programmer may use computer languages like C or COBOL or special purpose languages.
- data entry form
- A form which is designed to make it easy to enter new records.
 datasheet
datasheet- A view of database records that looks like a spreadsheet, with rows and columns
- data type
- The type of data is allowed in a field. There are several allowed data types:
AutoNumber: Assigns a number for each record automatically. The best way to be sure each record has a unique ID.
Text: Stores text and numbers and symbols, up to 255 characters.
Number: Stores numbers only.
Currency: Accepts numbers and formats as money.
Date/Time: Stores dates and times. Tricky to work with.
Memo: Accepts alphanumeric data. Use when you might need more than 255 characters. Cannot be sorted.
Hyperlink: Accepts alphanumeric text and formats as a hyperlink, like an email address or a link to a web page.
Attachment: Accepts one or more objects like photos or Word documents or PDF files. - DateAdd function
- An Access function which adds a certain number of intervals
to a date. The intervals can be years, months, days, hours,
minutes, seconds, quarters, weeks, or weekdays.
Syntax: DateAdd(interval, number, date)
where interval is a string expression that picks what kind of intervals you want to use. For example, "m" would be months, "d" would be days. number is how many intervals you want to add. A negative number would subtract, of course. date is the date to which you want to add.
Example:
DateAdd("yyyy",2,[PurchaseDate]) returns a date that is 2 years later than [PurchaseDate]. That might be when the warranty expires. - DateDiff function
- An Access function that calculates the difference between
two dates.
Syntax: DateDiff(interval, date1, date2)
where interval is how you want the difference reported - in years, months, days, etc.
date1 should be earlier than date2 to get a positive answer.
Examples:
DateDiff("d","3/4/1995", Now()) returns the number of days since Mar. 4, 1995. The answer will be different every day as time marches on!
DateDiff("yyyy",[BirthDate],[DeathDate]) returns the number of years from birth to death. - DatePart function
- An Access function that picks out a particular part of the
Date/Time, such as the year or the hour or the day of the week.
Syntax: DatePart(interval, date)
where interval is a string expression that tells Access which part you want to see. For example, "yyyy" would be the year. "h" would be the hour. date is the date or a string expression that identifies the value.
Examples:
DatePart("yyyy","January, 1, 2004") returns the value 2004.
DatePart("m",[DateHired]) returns the month portion of the value in the field DateHired. - Date/Time data type
- Stores a number and interprets it as a date/time value. There are several pre-defined formats such a Long Date (Monday, December 3, 2012), Medium Date ( 3-Dec-2012), Short Date (12/3/2012), Long Time (4:13:45 PM), Medium Time (4:13 PM), Short Time (16:13).
- default data
- Chart: Data that shows instead of data from actual records in Design View. Access cannot pull the records while in Design View.
- default value
- The value that a field will have if you do not enter a different value.
- Delete query
- An action query that deletes the selected records from a single table. Whole records are deleted even when only one field from the table is actually in the query.
- delimiter
- A character used to separate records or fields in a text database. Commonly, records are separated by a new line character, which does not show in the text document. Fields are usually separated by a comma (,), semi-colon(;), tab, space, or pipe character(|).
- Description
- Property of a field in a table. The text of the Description property shows on the Status Bar when the field is selected in a datasheet or form.
- detailed report
- A report which shows records, from the Detail section of the report's design.
- Detail section
- The section of a form or report in Design View that has the controls for showing records.
- dirty record
- A record that has been edited but the changes have not yet been saved.
- divider line
- A straight line which separates the sections or records of a form or report.
- documentation
- Includes a description of the design and properties of a database, database object, or programming code as well as how it should be used. Good documentation makes it clear what the design intended to do, why the particular design choices were made, and the consequences of changes that might be tempting.
- Documenter
- A feature of Access that creates a report for a database object that describes all of its properties.
E
- edit data
- To change existing data.
- ellipsis button
- A button with three dots
 which appears when you click in a Property text box
in the Property Sheet. Clicking the button opens
a window for creating a query or macro or expression
or mode segment.
which appears when you click in a Property text box
in the Property Sheet. Clicking the button opens
a window for creating a query or macro or expression
or mode segment. - embed
- To insert an object into a form or report, such as an image or subform or subreport or spreadsheet.
- embedded object
- A document or part of a document from one program that appears inside a document from another program. The embedded object does not show changes in the source document unless you manually update it.
- Enforce referential integrity
- Prevents a user from removing records that are joined to other records. This keeps your tables in sync.
- enter data
- Type data directly into a database table or in a form that will update the table.
- event
- An action that Access can identify and respond to, such as a mouse click, opening or closing a form or report, entering new data, the focus leaving a control.
- export
- Sending a copy of Access data or objects to another program or saving the data as a separate file.
- expression
- A set of characters, used to identify an object
in the database or to perform a calculation.
Expressions can be used in many places, such as
default values for field, validation rules, query
criteria, calculated fields and controls.
Examples:
Address2: [City] & " " & [Region] & " " & [PostalCode] concatenates text to form a new text field in a query.
OrderAmount: [Quantity] * [UnitPrice] does an arithmetic calculation for a new field.
Like "S*" in the criteria cell in a query will match with values starting with S. -
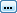
 Expression
Builder
Expression
Builder - A feature of Access that helps you create expressions by providing a list of available objects and functions. Having the syntax of the functions is particularly helpful. The illustration shows a function for a calculated column in the Scores table in the Language Arts Classes database. The function calculates the letter grade for a student's score.
- external data
- Data that is not in the current database.
F
- field
- A single item of data in a record like a date or a price or a score. In a spreadsheet database, the value in a single cell.
- Field List
- A list of the fields in the source for a form or report. You can drag these fields and drop them on the Design View of a form or report.
- field size
- The number of characters (text fields) or bytes (number fields) that a field is allowed.
- file size
- How much space a file takes up on the storage media. Usually measured in kilobytes (KB) or megabytes(MB).
- filter
- When a filter is applied, only records which match the criteria in the filter will be seen.
- Filter By Form
-
 A method for creating a filter which shows a single row datasheet.
What you enter in the cells acts as criteria. Applying the filter
hides records that do not match the criteria.
A method for creating a filter which shows a single row datasheet.
What you enter in the cells acts as criteria. Applying the filter
hides records that do not match the criteria. - Filter By Selection
-
 A quick method for creating a simple filter. The current field
value is the criteria for the filter so only records that share
that value will show in the datasheet.
A quick method for creating a simple filter. The current field
value is the criteria for the filter so only records that share
that value will show in the datasheet. - flat file database
- A database which puts all the data into a single table
- Fluent User Interface
- What Microsoft calls the new Office interface that uses ribbon tabs instead of tool bars and menus.
- footer
- Form Footer: An area that shows at the bottom of every form in Form View
Report Footer: An area that shows at the end of the report, after the last record
Page Footer: An area that shows at the bottom of each page of a report - foreign key
- A field in a table in a relational database which matches the primary key in a related table.
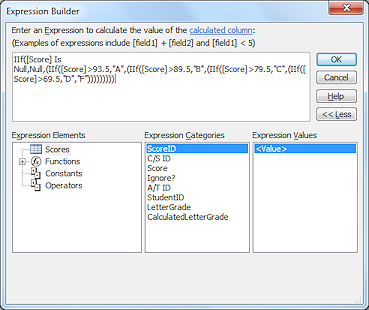
 form
form- A display of the fields in a record, usually showing all of
the fields in one window. When more space is needed, a form should
be designed to avoid horizontal scrolling by using subforms,
tabbed pages, or vertical scrolling.
- Form Header/Footer
- Sections of a form. The Form Header appears at the top of the form. If the forms are displayed as continuous forms, the header appears only once, before any form. The Form Footer appears below the form in Single Form view and after all records in Continuous Forms view. When printed, the Form Header appears before the Page Header. The Form Footer appears before the Page Footer.
- Form Wizard
- A sequence of dialogs which help you create a basic form quickly.
- formula
- An expression that calculates something, usually based on the
values in fields.
Example:
=[Price]+[Shipping] - Format Painter
-
 Clicking the Format Painter button changes the pointer to the
Format Painter shape
Clicking the Format Painter button changes the pointer to the
Format Painter shape .
The formatting of the current control is copied. When you click on
another control, the copied formatting is applied. Only certain
aspects of the formatting are copied.
.
The formatting of the current control is copied. When you click on
another control, the copied formatting is applied. Only certain
aspects of the formatting are copied. - Format function
- The Format function is used to change the default formatting of a value. It is often used to manage the display of dates and times.
- Syntax: Format(expression, format)
where expression identifies what you want to format and format is either the name of a standard format or defines how you want the value formatted.
Examples:
Format([Birthdate], "Short Date") returns a value like 4/5/1967.
Format(MyTime, "h:m:s") returns a value like 18:13:05.
Format(6547.4, "#,##0.00") returns a value with a comma separator, at least one digit to the left of the decimal and exactly 2 digits to the right, like 6547.40.
Format("Final Value", ">") returns FINAL VALUE in all caps. - Format Property
- A property of a field which defines how to display the values in that field. You can use pre-defined formats or create one of your own using special symbols. See Formatting symbols.
- frozen column
- A datasheet column that stays in view when the datasheet is scrolled.
- function
- A mathematical expression used in calculations, like SUM or COUNT or AVERAGE, or a logical expression, such as IIf.
G
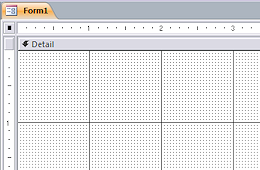 grid
grid- Form or Report Design: The dots and lines in Form or Report Design View which help you position the controls.
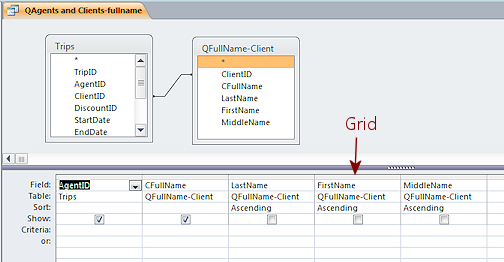 Query Design: The columns holding field names below the tables and queries that are part of the query.
Query Design: The columns holding field names below the tables and queries that are part of the query.
- group
- A set of records that share a value or whose values fall within a certain range.
- Group By
- A query will group the values of fields with Group By in the Total row and then calculate the "total".
- Group Header/Footer
- The header for a group in a report appears just before the records for the group. The group footer appears after the last record in the group. (See Report Header/Footer for illustration)
-
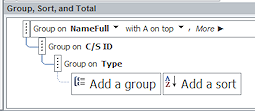
 Group, Sort, and Total Pane
Group, Sort, and Total Pane - Reports: A pane where you can select which fields to use to group your records and how to sort them.
H
- handles
- Squares that appear when a control is selected. Dragging a
handle will move or resize the control.


- header
- Form Header: Area that is shown at the top of every
form in Form View.
Report Header: Area that is shown at the beginning of a report before the first record.
Page Header: Area that is shown at the top of each page of a report. - Hide Duplicates property
- A property for controls on a report that hides repeated values. The records must be sorted to put the duplicates together in a sequence.
- HTML format
- File format for web pages
- hyperlink field
- A data type for hyperlinks.
I
- icon link
- A small icon that links to another document. Used in a document instead of embedding or linking
- identifier
- The part of an expression that refers to an object's value or
property. Depending on where and how you are using the expression,
the identifier may need parts.
Examples:
[Price]+[Shipping] uses the simple identifiers [Price] and [Shipping] to refer to fields in the current table.
Scores.AssignmentID > 67 uses the full identifier for the AssignmentID field that is in the Scores table.
Reports![Grades]![StudentName].Visible is the full identifier for the Visible property of the control StudentName that is in the report named Grades. - IIf function
- The Immediate IF function is an conditional function,
providing two different values, depending on whether an expression
is True or False.
Syntax: IIf(expr, truepart, falsepart)
where expr is an expression that can be said to be either True or False, truepart is the value you want to see when the expression is true, falsepart is what you want to see when the expression is false.
Both the truepart and falsepart are evaluated. Be careful that they won't generate an error, like trying to divide by zero.
Examples:
IIf([Balance] > 0, "You owe "& [Balance], "Paid") which would produce text like "You owe $858.93" or "Paid" - Image control
- A control on a form or report that contains an image. This is different from including an image in an Attachment data type control or inserting an image as an OLE object in an unbound OLE frame.
- import
- Bringing data or objects into a database from outside the database.
- index
- A feature of a database that puts the key fields in a table into order, like the index for a book. Sorting and filtering can be much faster using an index, rather than having to work with the original table and all its other data. The plural of index can be indexes or indices. Microsoft uses indexes.
- Input Mask Property
- A property of a field in a table. An Input Mask controls
what you see as you enter and edit data in the
field. It is a different property from the Format property, which
controls how values are display after they are saved.
See Examples and syntax
J
- join
- A join defines the relationship between two tables in a relational database. A join can be One-to-One, One-to-Many, or Many-to-Many.
- junction table
- A table that sits between two tables with a Many-to-Many relationship. Each of those tables has a One-to-Many relationship with the junction table. For example, in a classroom database, each student does many assignments and each assignment is done by many students. So tables for Students and Assignments cannot be joined directly. But a table Scores can be joined to both Students and Assignments. Each record in Scores is the score that one student earned on one assignment.
K
L
-
 label
label - Text that identifies what the data in a control represents.
- Label Wizard
- A sequence of dialogs that helps you create a mailing label report for a specific layout of labels on pre-cut, peel-off label stock. You need to know the manufacturer of the labels and the product number.
- layout
- The arrangement of parts for a datasheet, form , report, or the Relationships window.
- Like operator
- The Like operator is used to match data to a pattern.
You can use a specific value or wild card characters.
Examples:
Like "Tennessee" would match only the exact word Tennessee.
Like "T*" would match any word that starts with T.
Like "*ten*" would match any string that contains 'ten' anywhere in it, including the words Tennyson and attend and often. - link
- Web page: Text or an image that when clicked opens a new web page or performs an action.
- Access Table: Access can connect to a table in another Access database or to data in a another program. The outside table is "linked" to the database.
- Link Master Fields; Link Child Fields
- Properties which tell Access how to connect data for a form and subform or report and subreport. The form/report is the Master or Parent and the subform/subreport is the Child.
- linked object
- An object that will be updated if the original object changes. The source must be available, however, for this to happen. Databases may have links to tables in other databases. These tables will not be available if either of the databases has moved. Linked objects that are part of records, such as photos, are included in the database. They will update if the original photos changes. Linking to photos does not reduce the size of the database.
- Linked Table Manager
- A tool in Access for managing the links to tables outside of Access. If the links are broken, you must use the Linked Table Manager to relink.
- list
- A range in an Excel spreadsheet that is treated as a database by Excel. Once defined as a list, the columns in the range have drop-lists, there is a blue border around the range, a row for a new record is marked with a blue asterisk, the List toolbar appears with commands for managing the list.
 list
box
list
box- A control on a form which shows a list of choices in a fixed-size box. If the list is longer than can be displayed in the box, scroll bars appear.
- log file
- A text file that contains information about actions, such as errors or web server accesses or program updates.
- Long Text data type
- Name in Access 2013 for Memo data type. Allows for long text entries, up to 65,535 characters.
- Lookup field
- A field that lets you choose a value from a list instead of having to type in a value. The Table Design View includes the data type Lookup Wizard.
- Lookup Wizard
- A series of dialog pages that guides you through the steps to create a Lookup list for a field.
M
- macro
- A set of actions saved together that you can execute at an event. For example you could attach to a form button a macro that opens a particular report when the button is clicked.
- Macro Builder
- A dialog in which you can pick actions to create a macro.
- mailing labels
- A sheet of peel-off labels on which you print names with addresses. There are many different sizes of labels available.
- main form
- A form which contains a subform. Also called the Parent.
- main report
- A report which contains a subreport or subform. Also called the Parent.
- Main Switchboard form
- A form that opens when the database opens, usually containing links to open the forms and reports that are used the most.
- Make-Table query
- A query which creates a new table from the datasheet.
- margins
- The white space around the outside of what is displayed or printed. The Page Setup dialog controls the top, bottom, left and right margins of a page for printing.
- Max function
- A function which picks out the largest value in a particular
field in a query. For text values, Max picks the last value in
alphabetical order.
Syntax: Max (expr)
where expr is an expression that identifies the field or is an expression that does a calculation on that field
Examples:
Max([Price]) returns the largest number in the Price field.
Max ([FullName]) returns the last name alphabetically in the field FullName. - memo data type
- A text data type that allows for long text entries, up to 65,535 characters.
- metadatabase
- A database about other databases or that contains records of other databases.
- Microsoft Graph
- A program for creating charts from data. It opens only from inside another Microsoft Office program.
- Min function
- A function which picks out the smallest value in a particular
field in a query. For text values, Min picks the first value in
the alphabetical order.
Syntax: Min (expr)
where expr is an expression that identifies the field or is an expression that does a calculation on that field
Examples:
Min[Price]) returns the smallest number in the Price field.
Min([FullName]) returns the first name alphabetically in the field FullName. - modal
- A modal form or window requires the user to make choices or perform an action or else close the window before the user can switch to another window or form.
- modeless
- Not modal.
- module
- A collection of programming objects defined by the user using VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) code to automate tasks in the database.
- move
- To move objects in Design View of a form or report
-
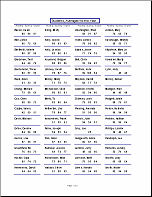 multiple
columns
multiple
columns - A report which arranges its records in two or more columns on a page. Records may go down the column and then across to the next column, or they may go across the row and then drop down to the next row.
N
- Navigation Form
- A form designed specifically to hold command buttons that open forms and reports in a subform. Especially useful for a web database because the normal Navigation Pane does not show in that case.
- Navigation pane
- Pane at the left of the Access window which displays database objects like tables, queries, forms, and reports.
- nested
- One inside the other.
- Expressions: One function can be nested inside
another function.
Example of IIf inside another IIf:
IIf([Date]>#1/1/2006#,[Date],IIf([Date]<#1/1/1999#,"<1999","Between")) - Forms/Reports: A main form or report contains a subform/subreport which itself contains another. Access allows up to 7 levels of nesting for subforms and subreports.
- normalized
- A database that meets certain design criteria is called normalized to a certain Form number. These criteria are intended to help keep the database speedy, logically organizes, and without errors. See Normal Form
- null
- A field that has no value is said to be null. It has never been touched. This is different from a field that contains an empty string. Both kinds of fields look the same in all views.
- number data type
- A field that can contain some kind of number. There are
several variations:
-
 Number - A general number comes in several number field sizes
including: Byte, Integer, and Long Integer.
Number - A general number comes in several number field sizes
including: Byte, Integer, and Long Integer. - Date/Time - A date is actually a number based on the number of days from December 30, 1899. Earlier dates are negative numbers. To calculate with dates it is important to use this format and not text.
- Currency - Use for high accuracy and for money. Avoids rounding. Can hold 15 digits to the left and 4 digits to the right of the decimal point.
- AutoNumber - Automatically assigns a unique number to each record. Great to use for an primary key.
-
O
- object
- An Access database is made up of objects, including tables,
queries, forms, macros, modules, sections, and controls.
Basically, an object is something that has a name that you can use
in a Visual Basic program. We primarily talk about the top level
of objects, which are the items listed in the Navigation Pane.
- Object Dependencies
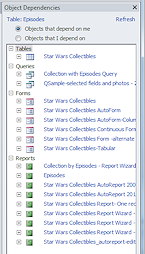
 A task pane shows a tree of dependencies for the selected object.
A task pane shows a tree of dependencies for the selected object.
The pane can show 'Objects that depend on me' or 'Objects that I depend on'.- object frame
- A control on a form or report which contains an OLE object like picture or spreadsheet. Consider using an Attachment field instead. The database won't increase in size nearly as much as with OLE objects.
- OLE object
- OLE = Object Linking and Embedding. An OLE object can be any external object or document, such as an image, a Word document, or an Excel spreadsheet. The program that created the object must support object linking/embedding. The program controls the display of the object and is required to edit the object, so the program must be installed on the same computer as the database. The new Attachment data type works better in most situations.
- operator
- A symbol or phrase that indicates what operation to perform.
Arithmetic operators include + for adding, - for subtracting, *
for multiplying, / for dividing and ^ for raising to a power .
Logical operators include AND, OR, NOT. Access has other
operators such as BETWEEN... AND...
-
 option
button
option
button - A control for choosing one of several choices on a form. Also called radio button, from the old style car radios which allowed you to jump to pre-selected radio stations by pushing a round button.
P
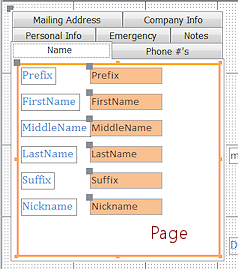 page
page- Tab Control: The rectangular area below the tab at the top of a tab control. A page can hold other control and labels.
- Page Setup
- A dialog in MS Access which has tabs for managing the printing: Page, Margins. For a report the dialog also has a tab for Columns
- Page Header/Footer
- In a form or report, the page header prints at the top of every page, except at the beginning of a report, where it prints below the Report Header. The page footer prints at the bottom of every page.
- Paint
- A basic graphics program that comes with Windows.
- parameter
- A parameter is a measurement or value that something else depends on. For example, the volume of a box depends on the parameters length, height, and depth. When the value of any of the parameters changes, the volume changes.
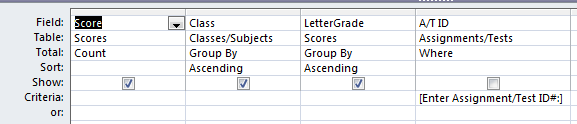 Parameter query
Parameter query- A query that asks for your input to set criteria before the query runs. You make the query ask by entering text between square brackets into the criteria row of the query design grid. When the query runs, a message box shows the criteria text and a text box for you to enter a value. It's a good idea to include hints about what to enter!
- Parent
- A form or report which contains a subform or subreport, which is called a Child.
- Paste Errors
- A table that is automatically created for data that failed to paste properly when running a query.
- path
- List of nested directories/folders that lead to a particular
file.
Example: E:\Docs\Computer Classes-RSCC\mylist.txt where the drive is E which has a folder named Docs which contains a folder named Computer Classes-RSCC which contains a file named mylist.txt. - pin
- An item that is pinned is fixed in place at the top of the list or to the Start menu or to the Taskbar.
- popup
- A window or dialog which appears on top of all other open windows. Popup ads are a notorious misuse of this useful feature.
- primary key
- A field which contains a value which is unique for each record in a table in a database. This field can be used to join two tables.
-
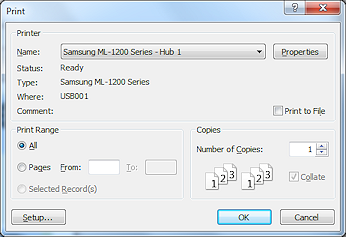 Print dialog
Print dialog - A dialog with which you can manage the actual printing process: choose a printer, access printer options, choose which pages to print, choose how many copies to print.
- Print Preview
- A view that shows how the table, form, or report will look when printed.
- propagating nulls
- If nulls are propagated, then whenever a part of a calculated value is Null, the whole
expressions is Null.
Example: Using + to concatenate values... [MyScore]:"The score is "+[Score] will be Null whenever the field Score is null, even though there is fixed text included. On the other hand, using the & in the calculation, like [MyScore]:"The score is "&[Score], will show the fixed text portion without a score, like "The score is ", when the field value is null. 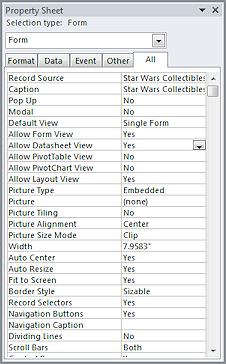 Property Sheet
Property Sheet- A pane which lists the properties of the selected object - a whole form or report, a section, a control. The pane contains several tabs, including an All tab which shows all available properties. Different objects have different properties.
- property
- An aspect of an object that you can change in its Property
Sheet.
Example: A control has properties like Name, Source, Height, Width, Back Color, Border Color, Border Style, and many more. - prototype
- A typical example or basis for constructing new instances.
- Label Wizard: an example label with placeholders for the parts of an address. It does not show any actual addresses.
Q
- query
- A method of selecting or organizing records in a database.
A simple query might sort records into alphabetic or numeric order
based on one or more fields. Another simple query filters the
records to show only those that match certain criteria, like LastName = Smith or NumberSold > 25.
The Design View shows a grid with a column for each field in the
query results. The Datasheet View is shows records in rows. Only
the chosen fields for the records that match the query's criteria
appear in the datasheet.
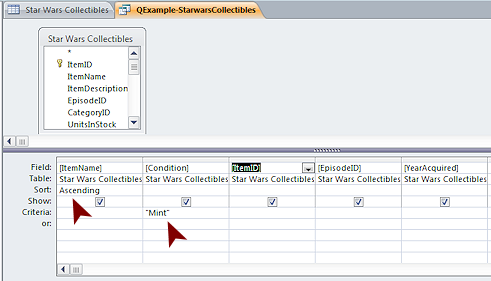
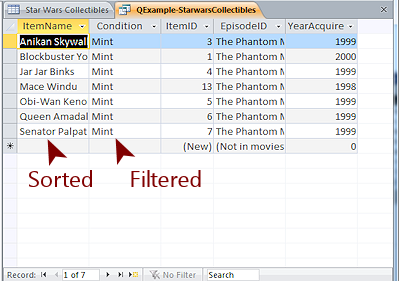
- Query Builder
- A design window for queries that opens from the Record Source property in the Property Sheet for a form or report. It looks very much like Query Design View. The query constructed can be saved as a new query or just saved as an SQL statement with the form or report.
R
- Read-only
- Able to display but cannot be changed.
- Forms: A form that is read-only will not allow the user to add records or edit records.
- record
- A set of fields which belong together, like a complete name and address or a complete sales order.
- record selector
- Area at the left of a datasheet or form that, when clicked, selects the whole record.
- Record Source
- A property of a form or report which tells where the records are coming from.
- referential integrity
- Making sure that records are not deleted or changed that are referred to by other records and that every object and field that is referred to, does actually exist.
- Regional Settings/Region and Language
- An icon on the Control Panel opens a dialog which lets you choose a language and country for your regional settings. This affects what Windows and Windows programs use as a unit of measure for distances and currency and also how dates and times are displayed.
- relationship
- A relationship defines how two tables are connected. Tables must share at least one field. A relationship can be One-to-One, One-to-Many, or Many-to-Many.
- relational database
- A database which uses several tables that are related by sharing a common field.
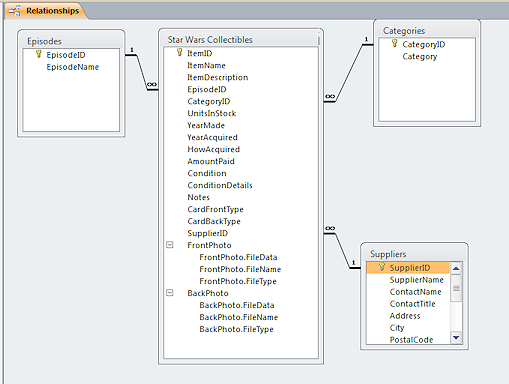 Relationships
window
Relationships
window- Displays related tables. Join lines show which fields are
matched between the tables.
- report
- A print-out which formats the records in a table or the
results of a query in a way that is easier to use than just
printing the datasheet. Reports can also group data for
calculations like counts and totals.
- Report Header/Footer
- A section of a report. The Report Header appears before anything else in the report. The Report Footer follows the last record and lies above the Page Footer.
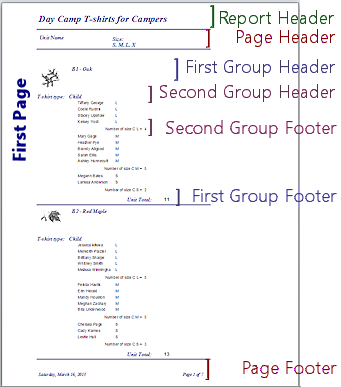
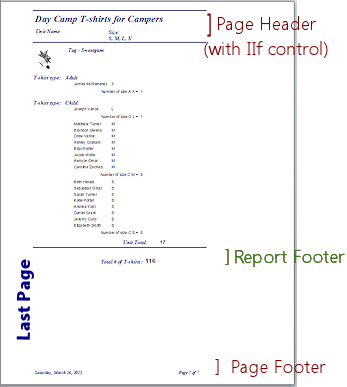
- Report Wizard
- A sequence of dialog pages that lead you through the process of creating a report.
- required property
- A property that must have a value for the record to be accepted.
- ribbon
- A section at the top of the window in a program using the Fluent User Interface. This area is taller than a typical toolbar and holds command buttons and galleries of choices.
- row
- A set of cells that runs across the page to the last column.
- row height
- The height of the cells in the row. All cells in the same row must have the same height.
- row source
- The table, list, or query that is the source for the choices in a Lookup list.
- RTF format
- Rich Text Format. A document format for word processing documents which retains a lot of the formatting of the document. Formatting that is specific to a particular word processing program will be lost but such things as font, font size, color, indentions are kept.
- run
- You run a Select query to display the datasheet of records that the query picks out. When an action query runs, the action is actually performed.
- running sum
- An accumulation of values from record to record. Each record adds its value to the sum of the values in the previous records.
S
- screen capture, screen shot
- An image of what was showing on the computer screen. Pressing the Print Screen key sends a image of the whole screen to the Windows Clipboard. Holding the ALT key down while pressing Print Screen key captures an image of the active window. You must paste the captured image into a graphics program or another program that can display graphics in order to see it.
- section
- A separate part of a form or report. Sections include header, footer, detail. Pages, reports, forms, and groups all have a header and a footer, though some sections may not be shown.
- Select query
- A query which selects fields from one or more tables or other queries. A select query can sort and filter the results based on criteria and can also include calculated fields, like FullName: [Firstname]&" "&[Lastname]
- selection
- The object that will receive the actions of keys and commands, such as a field in a datasheet or a text box on a form.
- shortcut
- An icon in a customized Navigation Pane that opens an object. These are used by database programmers who create custom navigation to help users find the items they use regularly and to keep them away from objects that should not be changed.
- Short Text data type
- Name in Access 2013 for Text data type. Allows alphanumeric entries up to 255 characters. Numbers entered in a Short Text field cannot be used in calculations.
- shutter bar
- A button that closes a pane side to side.
- sort
- To rearrange rows of data in an order without separating the fields in a record. The order can be alphabetical, numerical, or based on a custom list.
- Sort Ascending
-
 A button which will sort selected cells in a column into
alphabetical or numerical order. If multiple cells are selected
in each row or whole rows are selected, the sorting is based on
the first cell in each row of the selection.
A button which will sort selected cells in a column into
alphabetical or numerical order. If multiple cells are selected
in each row or whole rows are selected, the sorting is based on
the first cell in each row of the selection. - Sort Descending
-
 A button which will sort selected cells in a column into
reverse alphabetical or numerical order. If multiple cells are
selected in each row or whole rows are selected, the sorting is
based on the first cell in each row of the selection.
A button which will sort selected cells in a column into
reverse alphabetical or numerical order. If multiple cells are
selected in each row or whole rows are selected, the sorting is
based on the first cell in each row of the selection. - Sort dialog
- A dialog which offers more choices than the Sort buttons to sort a datasheet. You can sort on 3 different columns. For each one you can choose to sort ascending, descending, or use a custom list.
- source
- The table and/or queries that the data comes from for a form, report, or data access page.
- spreadsheet
- Sheet or worksheet. Formed of rows and columns.
- spreadsheet database
- A range in a spreadsheet that can be treated as a database, having each record in its own row.
- SQL
- Structured Query Language is a language
used to select and organize records
in a database. For example, when the parts of a student's name are in separate
fields in the table named Students, a query can put the parts
together, group the records by class, and alphabetize them with
the following in SQL:
SELECT Students.StudentID, Students.LastName, Students.FirstName, Students.Class, [LastName] & ", " & [FirstName] AS Name
FROM Students
ORDER BY Students.Class, [LastName] & ", " & [FirstName]; 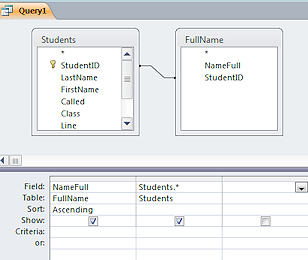 SQL statement
SQL statement- A query shown in SQL instead of in a design grid. For example,
the following SQL statement is the same as the query design in the illustration:
SELECT FullName.NameFull, Students.*
FROM Students INNER JOIN FullName ON Students.StudentID = FullName.StudentID
ORDER BY FullName.NameFull;
- square brackets
- Symbols surrounding a field name, like [Price].
left square bracket = [
right square bracket = ] - Stacked layout
- A layout for a form where field controls are arranged in a table. Resizing one control will resize all the controls in the same column.
- standard height
- The standard, or default, height for a row in a datasheet is based on the font used. The standard height
14.25 points for the default font, Calibri.
1 point is 1/72 of an inch. - standard width
- The standard, or default, width for a column in a datasheet is 1 inch, measured on a printed copy.
- stretch
- To enlarge an image to fit the size of its control, without trying to keep the proportions the same as the original image.
- string, or text string
- A set of text characters, as opposed to a number. The formatting of strings may be different from the formatting of a number with the same characters. For example, as a text string, 49.56 is aligned to the left, but as a number it would be aligned to the right.
- subdatasheet
-
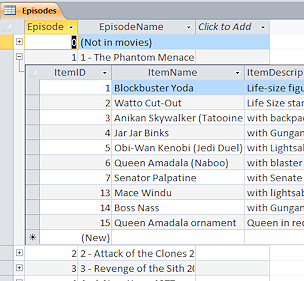 A
datasheet inside a datasheet. When two tables have a One-to-Many
relationship, the datasheet of records in the table on the One
side can open a subdatasheet that shows the related records.
A
datasheet inside a datasheet. When two tables have a One-to-Many
relationship, the datasheet of records in the table on the One
side can open a subdatasheet that shows the related records.
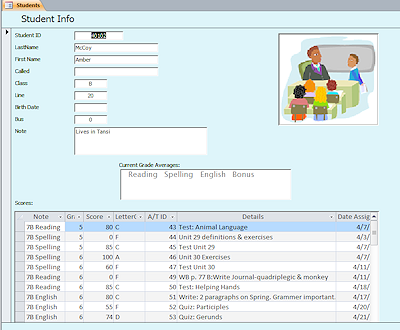 subform
subform- A form which is itself a control on another form or report.
- subreport
- A report which is itself a control on another report. A subreport cannot be put onto a form in Access 2007 but can in Access 2010.
- Sum function
- Adds all of the values in a field or the calculations based on
a field or fields.
Syntax: Sum(expr)
where expr is a field name or expression.
Example: Sum([Score]) would add all of the scores together. - summary report
- A report which contains summary information but no detail records. Such a report might contain only a chart or only totals.
- switchboard
- A form which allows you to click buttons to perform actions or open selected forms and reports. A switchboard can have multiple pages, which look like separate forms.
- Switchboard Manager
- A tool in Access for creating and managing a switchboard form and its pages. Only one switchboard form can exist in a database. You can create the same effect yourself by creating custom dialogs. In Access 2010, the command to open the Switchboard Manager is not shown on any ribbon. You can add it to the Quick Access Toolbar. Look in the list of Commands Not on the Ribbon.
- switchboard pages
- A switchboard form can include buttons that open other pages of the form. For example on the main switchboard page a button called Forms could open another page that has buttons for the most commonly used forms in the database.
- synchronize
- To coordinate. In particular, a subform or subreport synchronizes with the main form or main report to show only the records that match the current record.
- syntax
- The rules or pattern for constructing an expression or
function.
Example: A calculated value in a query has the general form: NewFieldName:expression - Example: The IIF function has the general form:
IIF(<statement that is either true or false>, <value if true>, <value if false>)
T
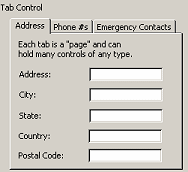 tab
control
tab
control- A control on a form which shows two or more tab pages.
- tab page
- Each tab displays a different page in a tab control.
- table
- A set of records in rows and columns
- template
- An object that is used to create a new object. A table template for example creates a new blank table with a set of pre-designed fields.
- text box
- A control on a form or report that contains text or numbers. Values can be entered on a form by typing in the text box.
- Text data type
- Stores alphanumeric text (including numbers and symbols). Maximum field size is 255 characters. Numbers in a text field cannot be used in calculations.
- texture
- An image that is tiled across the background, usually creating the impression of a single surface. The effect may be of wood, steel, water, stucco, fabric or just a design.
- theme
- A set of fonts, colors, bullets, and backgrounds. If you chose your fonts and colors from a theme, then changing the theme changes those items to match the new theme.
- tiling
- Repeating a small image across the screen and then dropping down to repeat across the screen again.
 toggle
button
toggle
button- An option button which switches a value on or off. In Access forms, these behave the same as option buttons or check boxes, which is not true in web pages for similar-looking buttons.
- Total row
- A row in a Query Design Grid that appears when you change a query to a Totals query. The choices for what kind of total to create include Sum, Average, Count, Max, Min, and several others.
- truncate
- To fail to show all of the the characters in a value. This happens if the control is not wide enough.
U
- unbound control
- A control that does not have the Control Source set. These are used in custom dialogs to receive input from the user.
- unbound object frame
- An object frame which is not tied to an object that will change for each record. The contents of the frame will be the same for all records.
- Update query
- A query which updates values in selected fields.
V
- validate
- To confirm as acceptable, appropriate, or correct.
- Validation Rule
- A property set in the Table Design view-
- Table: The validation rule for a table applies to the
table's records. A record will not be saved unless it satisfies
the validation rule. Such a rule may involve several different
fields in a comparison or calculation.
Field: The validation rule for a field is applied when the field's value is saved. An entry will not be saved unless it satisfies the rule. - Validation Text
- A property set in the Table Design view -
- When a validation rule is violated, a message box displays the Validation Text, which should explain what kinds of values are acceptable.
- value list
- A list of values to use as the Row Source for a Lookup field. A user selects a value from the list when entering or editing a new record.
- View: Datasheet
- A view where you see the records as a set of rows and columns.
- View: Design
- A view where you can add, delete, move and otherwise edit a form, report, or data access page.
- View: Form
- A view where you can see a form with data displayed.
- View: Layout
- A view of a report which shows record data while still letting you make some kinds of changes to the layout. For example, you can resize a control that is not showing all of the text, like a name or address. In Design View you cannot see the data so you have to guess at how wide the control must be. Some changes cannot be made in Layout View.
- View: Print Preview
- A view that shows the whole document, page by page, as it will be printed.
- View: Report
- A view that shows how the data will display but does not break up the report into the paper pages that would print. You can scroll the whole report.
- Visual Basic
- A programming language, Visual Basic for Applications, which can be used to automate many actions inside Access.
W
- watermark
- A background image on a form or report that stays in one place rather than tiling across the whole background.
- wild card character
- A character/symbol which is a placeholder in an expression. See the article Wild Card Characters for uses and choices.
- wizard
- A set of dialog pages that walks you through the choices to make to create something, such as a control, form or report.
X
- .xls, .xlsx
- The file extension used for Excel spreadsheets.
- XLS or XLSX format
- File format used for Excel spreadsheets
Y
Z
- zero-length string
- A character string without characters, indicated by two double-quotes with nothing between them, "". A field would have such a value when you KNOW that the record has no value for this field. This is different from a NULL value, which has never been set and means more like "I don't know whether or not this field should have a value."
- zoom
- Print Preview: To
enlarge or reduce the size of the print preview of a report. When the mouse pointer has a Zoom shape,
 or
or  , clicking toggles between enlarging and reducing the view. On the Status Bar there is a slide control for Zoom. On the Print Preview ribbon tab there is a drop list of percentages and the choice Fit to Window, which
makes the report fit into the window as a whole page.
, clicking toggles between enlarging and reducing the view. On the Status Bar there is a slide control for Zoom. On the Print Preview ribbon tab there is a drop list of percentages and the choice Fit to Window, which
makes the report fit into the window as a whole page. - Property Sheet: A choice for Size Mode property for an image
which sizes the image to fit the control but keeps the original
proportions of the image.
- Zoom window
-
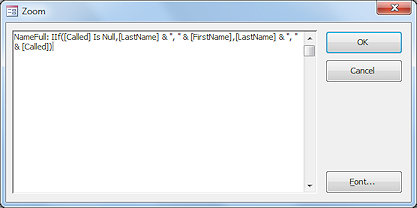 A
handy popup window with blank space where you can compose an
expression for a calculated field in a query. It has much more
visible space that the Query Design grid and is less complicated than the Expression Builder window.
A
handy popup window with blank space where you can compose an
expression for a calculated field in a query. It has much more
visible space that the Query Design grid and is less complicated than the Expression Builder window.
