Buttons on the Formatting Bar
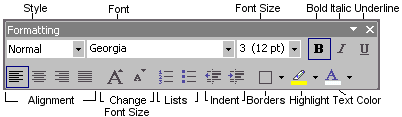
 You may click on a button above to skip down to its description below.
You may click on a button above to skip down to its description below.
 Style
Style
 Has
a list of the basic HTML block elements, those
that start a new paragraph. Has
a list of the basic HTML block elements, those
that start a new paragraph.
You have already used some of these HTML styles: Heading
1, Heading 2, Definition, Defined Term, Bulleted List, and Numbered List.
HTML Code: Selecting a style from the list
surrounds the whole paragraph that the cursor is currently in with the
selected tag, like:
<h1>This is a title</h1>.
In FrontPage you create new styles with
Cascading Stylesheets (CSS).
This feature is not covered in HTML Basics.
 Font
Font
Drops a list of the fonts installed on the computer.
HTML Code: Choosing a font will apply it to the
selected text by surrounding the text with a font tag, like:
<font
face="Times New Roman">This is formatted with Times New Roman</font>.
Consider carefully when deciding to pick a specific font.
If that font is not installed on the computer that is used to view
the HTML document, the browser will use its default font instead. The newer
HTML recommendations use Cascading Stylesheets (CSS)
to assign a font instead of using the <font> tag. The FONT tag
has been deprecated, which means this tag is
considered to be out-of-date and future browsers may not understand it.
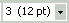 Font Size
Font Size
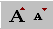 Increase/Decrease Font Size
Increase/Decrease Font Size
HTML Code: In HTML you can only set a relative
font size from 1 to 7 by adding the SIZE attribute
to the FONT tag, like <font size="4">.
The default font size is 3. Other sizes are actually a percentage
of the default size.
The Font Size box
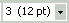 shows both a point size and an HTML size. The point size is an estimate
of the size you will see. It does not mean that even a print-out will be
that exact size.
shows both a point size and an HTML size. The point size is an estimate
of the size you will see. It does not mean that even a print-out will be
that exact size.
The Increase and Decrease Font Size buttons
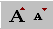 do not assign a specific point size to the selected text. They just change
the size up or down 1 size.
do not assign a specific point size to the selected text. They just change
the size up or down 1 size.
 Different
fonts at the same font "size" do not actually appear on the page as the same
physical size! The samples below show Times New Roman and Arial in sizes
from 1 to 7. Quite a difference in the larger sizes, in both width and
height! Different
fonts at the same font "size" do not actually appear on the page as the same
physical size! The samples below show Times New Roman and Arial in sizes
from 1 to 7. Quite a difference in the larger sizes, in both width and
height!

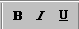 Bold,
Italic, Underline Bold,
Italic, Underline
HTML Code:
These buttons surround the selected text with
character formatting tags:
Bold= <b> </b>
Italics = <i> </i>
Underline = <u> </u>
Some other WYSIWYG editors will use the logical
formatting tags <em> and
<strong> instead.
 Font Color
Font Color
Clicking the Font Color button
 applies the color shown in the bar under the A on the button. Clicking
the down arrow at the right of the button opens a palette of color
choices. You can pick a color that is not shown by clicking the More
Colors... link at the bottom of the palette.
applies the color shown in the bar under the A on the button. Clicking
the down arrow at the right of the button opens a palette of color
choices. You can pick a color that is not shown by clicking the More
Colors... link at the bottom of the palette.
HTML Code: The selected text is surrounded
with a FONT tag with the COLOR attribute. The value is a
hexadecimal number, like:
<font color="#FF0000">This text is red.</font>.
Some colors also have names, but not all browsers
understand color names. Using the hexadecimal number is safer. |
|

Color palette
in FrontPage 2002 |
Color Numbers
The number for each color comes from the hexadecimal numbers (that is,
base 16) for how much red, green, and blue are needed to make the color. 255
gives the maximum amount of a color. 255= FF in hexadecimal (base 16)
numbers. Of course, 0 would mean that none of that color.
Example 1:
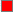 from row 2, 3rd from the right, in the FP 2002 color palette
from row 2, 3rd from the right, in the FP 2002 color palette
The color number for this red is #FF0000. That means it has the maximum
amount of red (FF), no green (00), and no blue (00).
Example 2:
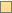 row 5
at the far right in the color palette row 5
at the far right in the color palette
The color number for this soft yellow color is #FFDE94. That means it has
maximum red (FF) and some green and some blue.
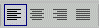 Alignment: Left, Center, Right, Justify
Alignment: Left, Center, Right, Justify
The Alignment buttons add the ALIGN attribute
to a block element tag in order to align the text. There are actually four
values for alignment: left, center, right, and
justify.
HTML Code: Selecting an alignment button adds the ALIGN attribute to block element tags like
<p>, <h1> and <li>, which apply to
whole paragraphs.
<p align="left">
<p align="center">
<p align="right">
<p align="justify">
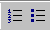 Lists
Lists
The List buttons turn your selected text into a list with either numbers
or bullets. You can format the style of numbering or bullet shape from the
menu | .
For numbered lists you may choose whether to number as 1, 2, 3 or
I, II, III or A, B, C or a,b,c or i, ii, iii.
For bullet lists you can choose a solid disc, an open circle, or a
square. You can also use a picture for a bullet shape.
HTML Code: The tags <ol> </ol> or <ul> </ul>
start and stop the list. Each item in the list is marked with <li>.
 Indent Indent
The Indent buttons increase or decrease the amount that the selected text
is indented.
HTML Code: The block element that the cursor is in is surrounded
by the tags <blockquote> </blockquote>. To get a deeper
indention, BLOCKQUOTE tags can be nested.
Disadvantage: You cannot use basic HTML to adjust the amount of indention that
each <blockquote> adds. You must advance to Cascading
Stylesheets to set indention amounts to suit yourself. It is actually a
violation of the intention of the BLOCKQUOTE tag to use it for spacing. It
is supposed to be used for text that you are quoting from somewhere else.
 Borders
Borders
The Borders button adds a border around the selected block
elements, those that create a new paragraph.
HTML Code: The selection is surrounded by a DIV (division) tag
with a complex STYLE attribute, like:
<div style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1; padding-left: 4;
padding-right: 4; padding-top: 1; padding-bottom: 1"> This line should have
a border.</div>
The code should produce the sentence below with a border extending from
edge to edge.
This line should have a border.
The STYLE attribute is a way to apply stylesheet formatting to a
particular spot on your page.
 Highlight
Highlight
Clicking the Highlight button applies the color shown on the button as a
background to the selected text. Clicking the arrow opens a palette of
colors.
HTML Code: The selection is surrounded by a SPAN tag with a COLOR
attribute, like:
<p>This sentence has <span style="background-color:
#FFFF00">highlighted words</span>.</p>
The code should produce the sentence below with the last two words on a
yellow background:
This sentence has highlighted
words.
|
 Formatting Bar
Formatting Bar
![]()
![]()